Last month while Jill and I were in Texas we visited NASA’s Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center in Houston. Accompanying us were Derek, Sarah, and Bryson. The Center is the hub for human spaceflight activities. There are 100 buildings on 1,620 acres that are home to the U.S. astronaut corps. The Johnson Space Center was originally known as the Manned Spacecraft Center and was constructed on land donated by Rice University. In 1973, the center was renamed after Lyndon B. Johnson, 36th President of the United States.
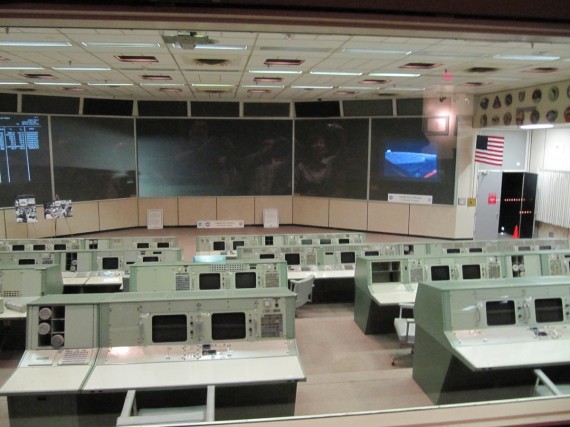
Mission Control Center
We started out our visit at Space Center Houston, the official visitor center for the Johnson Space Center. We procured a place on the guided tram tour with a first stop at the Mission Control Center (MCC). Since 1965 the MCC has been the nerve center for America’s manned space program. The MCC houses several Flight Control Rooms, from which flight controllers coordinate and monitor the spaceflights.
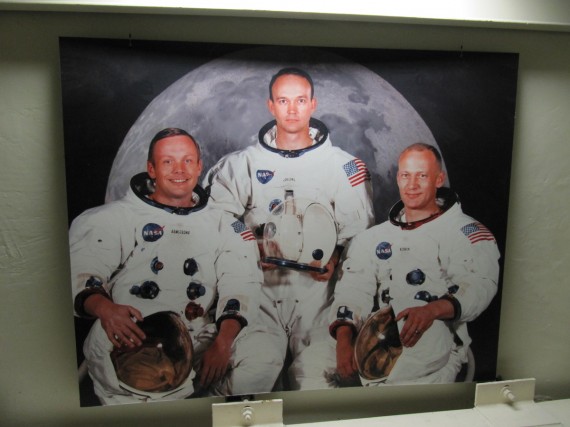

Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin, crew of Apollo 11, pictured on the stairs to the MCC
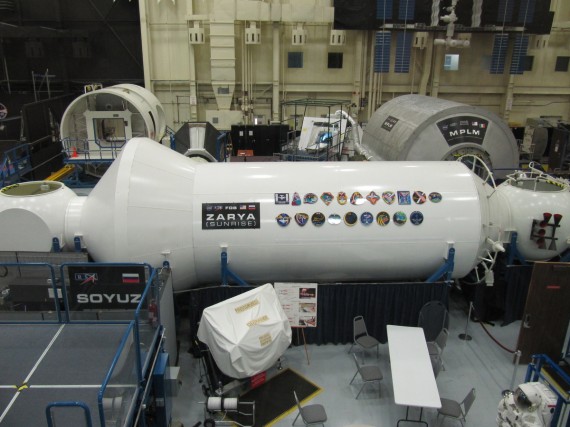
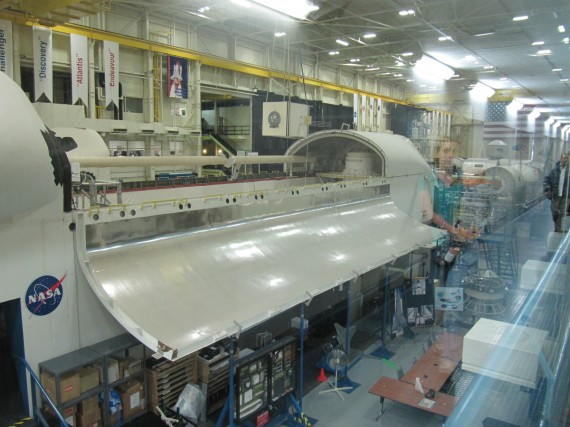
Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility
After the MCC, we visited the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility. The crews for each mission put in up to 100 hours training in this giant building. There are full scale mock-ups for different aspects of the Space Shuttle Orbiter and International Space Station.
The Full Fuselage Trainer is a full-scale mock-up of the Shuttle, but without the wings. It has a full sized cargo bay area big enough to hold a bus. The Crew Compartment Trainers allow astronauts to learn how to operate many of the orbiter sub-systems.
Rocket Park
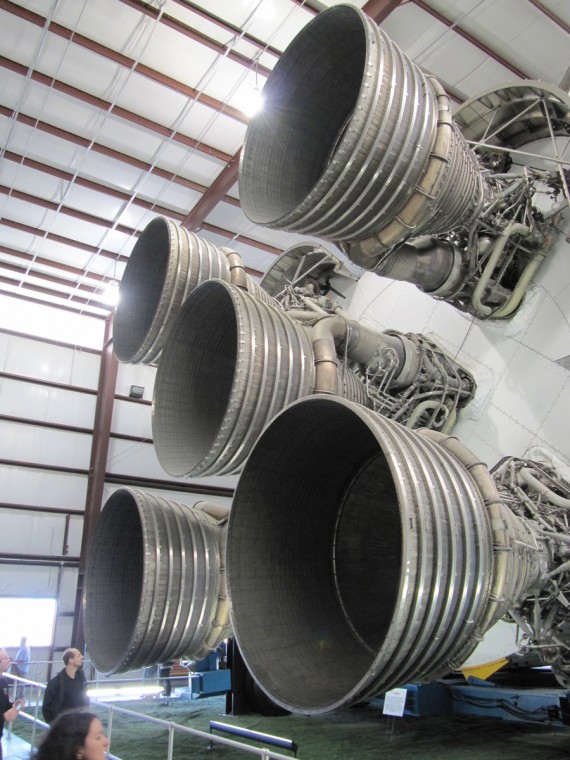
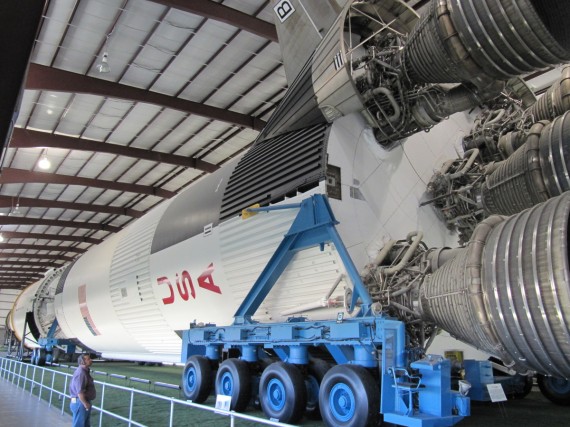
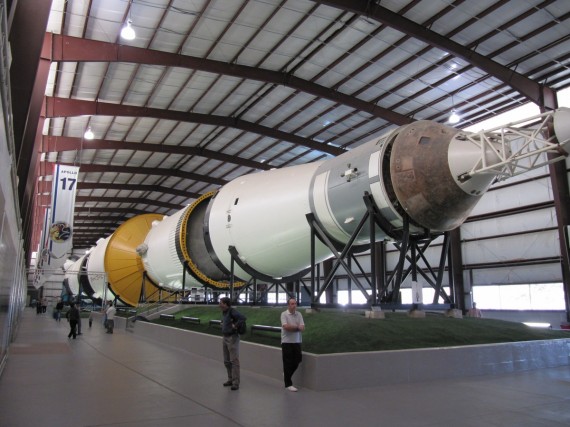
Next on the tour was Rocket Park. There are several rockets and rocket engines on display outside the Saturn V building but the most interesting is the Saturn V inside the building. The Saturn V was a multistage liquid-fuel expendable rocket used by NASA’s Apollo and Skylab programs from 1967 until 1973. It remains the largest and most powerful launch vehicle ever brought to operational status from a height, weight and payload standpoint.
The Saturn V stood over 363 feet high and weighed over 6 million pounds. It remains the largest and most powerful U.S. expendable launch vehicle ever built. From 1964 until 1973, a total of $6.5 billion ($43.57 billion in current dollars) was appropriated for the Saturn V, with the maximum being in 1966 with $1.2 billion ($8.04 billion in current dollars).
Apollo
After disembarking from the tram we watched the film “On Human Destiny” in the Destiny Theater. After that we looked in on the Starship Gallery to see such things as the Lunar Module replica, the actual Gemini V capsule, and the last flown Mercury Capsule. I was most interested in the Apollo program and the Lunar Rover Trainer used to prepare astronauts for the Apollo 15, 16, and 17 missions.
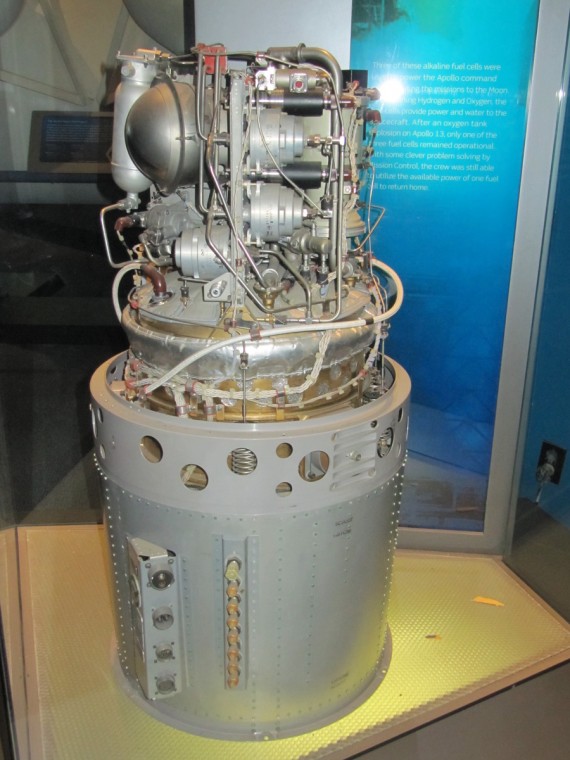
Three alkaline fuel cells were used to power the Apollo command module during the missions to the Moon. By combining hydrogen and oxygen, the fuel cells provide power and water to the spacecraft. After an oxygen tank explosion on Apollo 13, only one of the three fuel cells remained operational. With some clever problem solving by Mission Control, the crew was still able to utilize the available power of one fuel cell to return home.
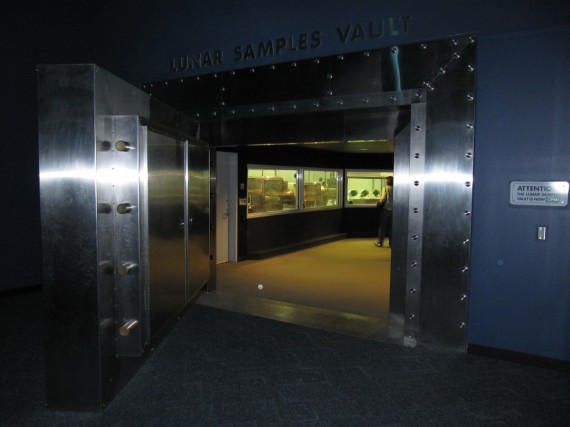
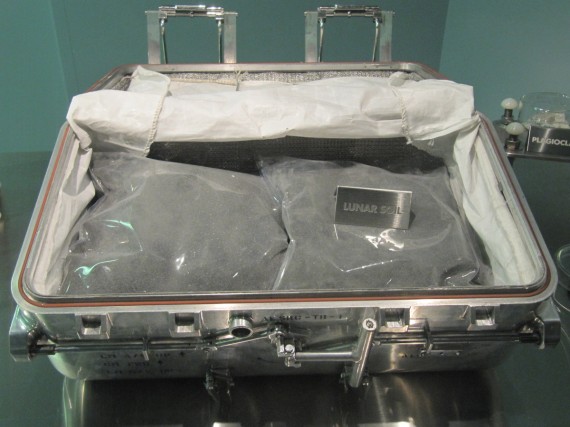
The world’s largest public display of Moon rocks are housed in the Lunar Vault where visitors can touch a 3.8 billion-year-old piece of the Moon brought back to Earth by Apollo 17. According to the Houston Chronicle of July 15, 1969:
Space agency officials jubilantly hailed the success of Apollo 11 while a priceless cargo of lunar dust and rocks was flown to the Manned Spacecraft Center today.
One box of Moon rock … contained material from five inches below the surface and other surface samples for a total of about 20 pounds.
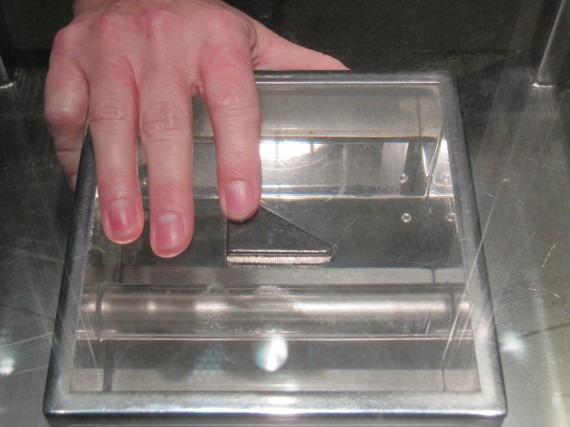

Jill touching a piece of Moon rock obtained in the Valley of Taurus-Littrow. This rock is basalt, formed by the cooling of molten lava.
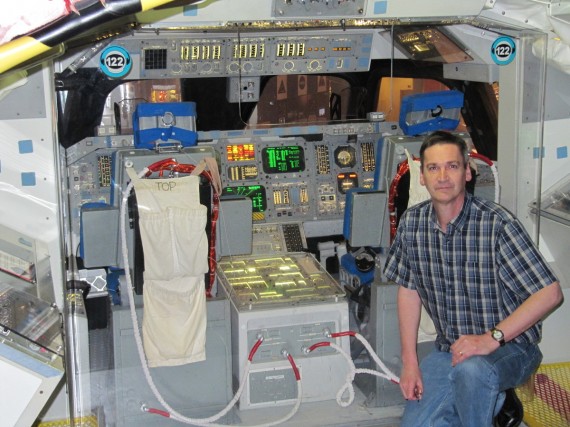
Space Shuttle
You can climb aboard a full-scale mock-up of the forward section of a space shuttle orbiter. The controls on the flight deck and the equipment on the mid-deck are exact replicas of the Space Shuttle Endeavour’s on her maiden voyage in May 1992.